Cascading effect of tax means a tax on tax. It is a situation where a consumer has to bear the load of tax on tax and inflationary prices as a result of it. It occurs when a good is taxed on every stage of production and distribution, and each succeeding transfer of good is taxed inclusive of the taxes charged on the preceding transfer. For example,
if a manufacturer pays excise duty on a product and then sells it to a wholesaler, who pays VAT on the product and then sells it to a retailer, who pays sales tax on the product and then sells it to a consumer, then the consumer is paying tax on tax at each stage. This leads to higher prices and lower efficiency in the economy.
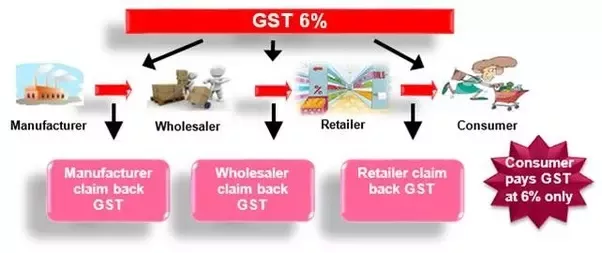
GST eliminates the cascading effect of tax by allowing input tax credit for the taxes paid on inputs used in the production or supply of goods and services. This means that only the value addition at each stage is taxed, and not the entire value of the product. This reduces the tax burden on the final consumer and improves the competitiveness of businesses.
How will be GST reduce the cascading effect?

- Imposing a single tax on goods and services across the supply chain, instead of multiple taxes at different stages.
- Allowing input tax credit for the taxes paid on inputs used in the production or supply of goods and services, which can be offset against the output tax liability.
- Levying tax only on the net value added at each stage of the supply chain, and not on the entire value of the product.
- Eliminating taxes such as excise duty, VAT, service tax, CST, etc. that caused double taxation and increased the cost of goods and services.